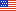
Caves and Karst
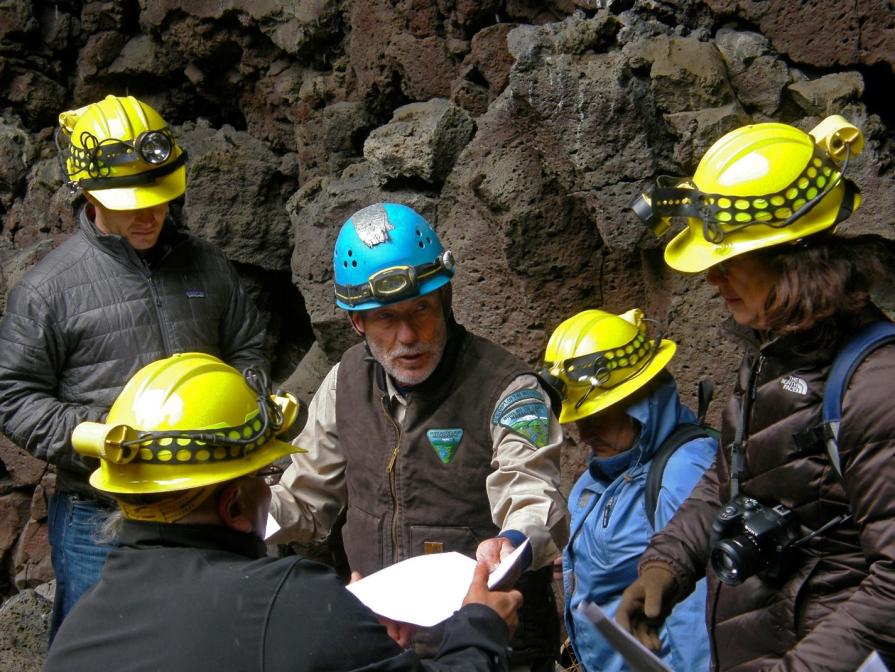

The BLM’s Cave Resources program was established to do the following:
- Provide for recreational and primitive caving opportunities.
- Ensure maximum consistency and continuity in the management of cave resources.
- Identify where these resources are located.
- Manage them to protect their inherent values in accordance with the Federal Cave Resources Protection Act of 1988.
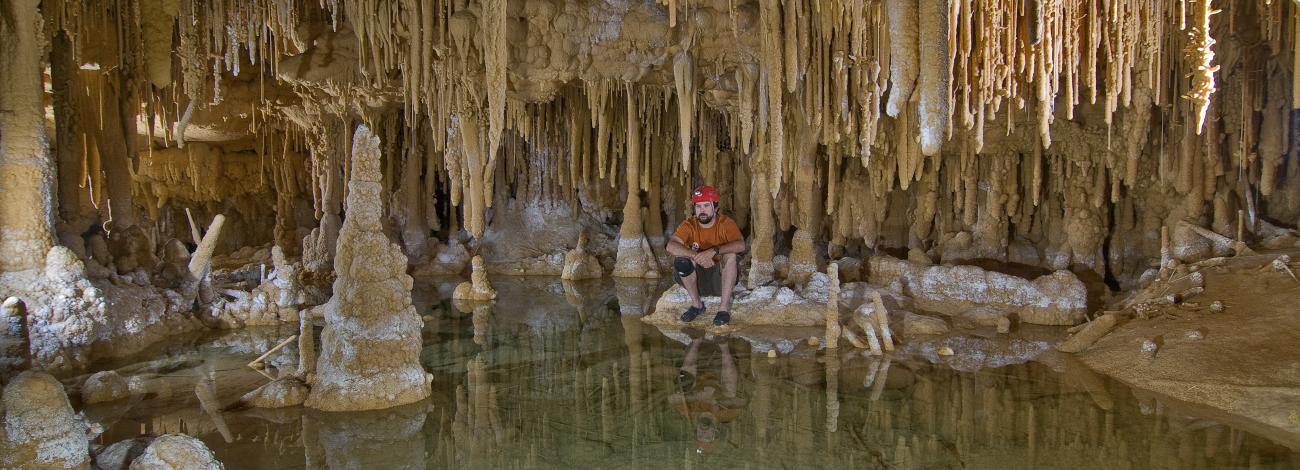
The BLM manages several thousand caves, primarily in karst (limestone) regions. Caves are a fascinating and fragile world that is an important resource for scientific and historical research and environmental education. Caves also provide habitat for bats and other wild creatures. Some caves on BLM public lands are also available for public exploration and may require a permit.
The BLM relies on volunteers and special interest groups to locate, survey, inventory, and monitor its cave resources, and provide critical feedback regarding the management of those resources across all disciplines.
Caves conjure wonder and awe. They offer a unique blend of geological wonders, ecological habitats, and historical significance, making them distinct from other natural environments. Their subterranean nature provides a constant and stable environment, unlike the dynamic conditions on the surface, fostering specialized ecosystems and unique geological formations. Caves have served as shelters and sites of cultural and religious significance for humans throughout history, adding another layer of uniqueness.
Caves are a part of a larger underground drainage system. Karst is a term that describes the landscape and processes that involves formation of caves. This landscape is where the dissolving of enlarged water flow paths within the bedrock has created caves, sinkholes, sinking streams, springs, and other characteristic features. Karst is associated with soluble rock types such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum. Karst landscapes can present unusually issues – fast underground transportation of contaminants, sinkhole collapses, and unusual flooding conditions.
Bureau of Land Management (BLM) is directed by the Federal Cave Resources Protection Act of 1988 to inventory, collaborate, and protect significant caves. The objectives of the BLM’s cave and karst resource management policy from the BLM Manual 8380 approved in 2008 are to:
A. Provide a framework to identify, evaluate, manage, monitor and protect cave and karst resources on public lands for the purpose of maintaining their significant, fragile and nonrenewable biologic, geologic, mineralogic, hydrologic, cultural, paleontological, scientific, scenic, and recreation values for both present and future uses.
B. Establish adequate surface and subsurface management practices to ensure the long- term protection of cave and karst resources.
C. Ensure that actions related to cave and karst resources requiring authorization or approval by the BLM are consistent with the BLM mission of multiple use and sustained yield.